Choosing between raster and vector pictures matters a lot in the digital design world. It’s not just a tech thing; understanding raster vs vector is essential for making things look great on online or in pictures. Knowing the differences helps designers fix problems with picture size, quality and how well they work together. For example, if you need a detailed photo for your project, choose a raster image like JPEG. But, for logos or icons that must look good at any size, go with a vector image like SVG.
In This guide you can get knowledge about raster vs vector graphics and when to use each type.
What is Raster Image?
A raster image is a type of digital picture made up of tiny dots called pixels. Each pixel has color information, and all the pixels together create the complete image. Examples of raster images include photos from cameras or pictures scanned into a computer. They’re good for detailed pictures, but if you make them bigger, they might not look as good. Unlike vector images that use math for shapes and don’t lose quality when resized. Common raster formats are JPEG, PNG, GIF, and BMP.
What is Vector Image?
A vector image is a digital picture made with math, not tiny dots. It uses points and paths to create shapes. Unlike pixel-based pictures, vectors stay sharp no matter how big or small. Good for logos and illustrations. Formats like SVG, AI, and EPS are common. Resize easily without losing quality.
What are the differences between raster and vector images?
Raster and vector graphics are two important image formats. They each have their way of doing things. Let’s explore raster vs vector and see what sets them apart!
Resolution
Raster:

Raster images, made up of tiny dots (pixels), have a fixed resolution. When you enlarge them, the dots get bigger, leading to a decrease in image quality. Think of it like zooming in on a photo—eventually, you see the individual dots, and things may look less sharp.
Vector:
Vector images don’t have a fixed resolution because they use mathematical formulas to create shapes. Regardless of size changes, vector images remain sharp and clear. It’s like resizing a drawing without losing any details, as there are no fixed dots to become pixelated.
Suggested Article- Image Resolution on Vector Conversion
File Size
Raster:
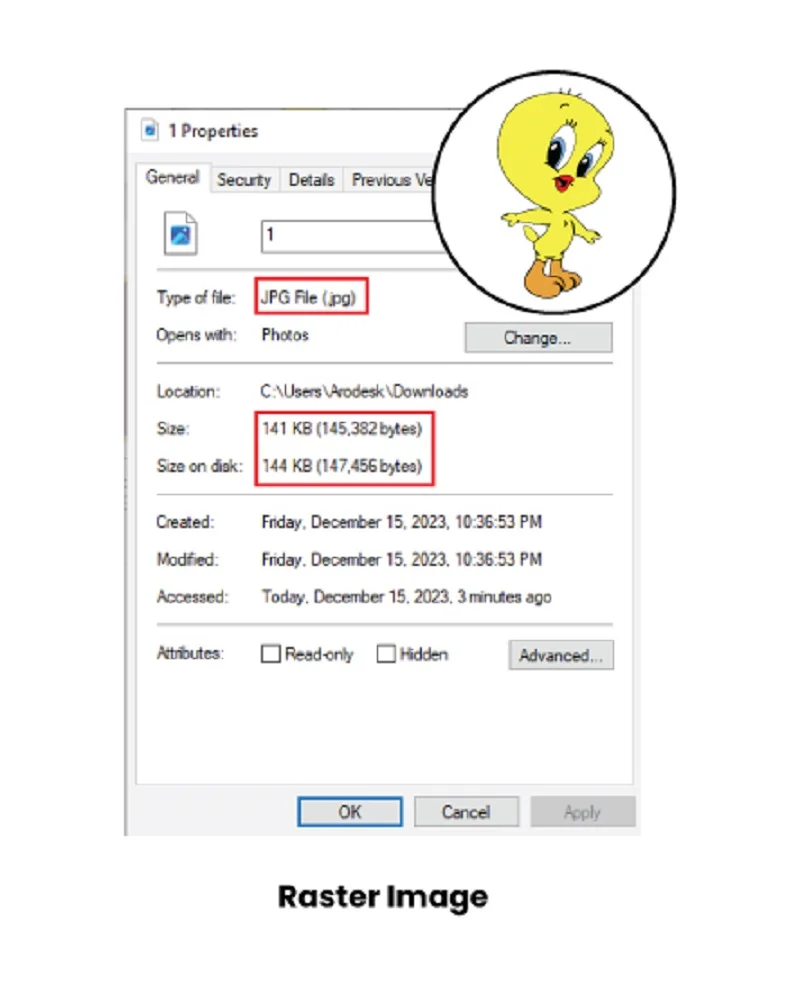
Imagine a raster image like a big collection of tiny dots, each holding a color. The more dots, the larger the file. So, if you have a detailed photo, it might have lots and lots of these dots, making the file pretty big. This matters when you want to share or store pictures because big files take up more space.
Vector:
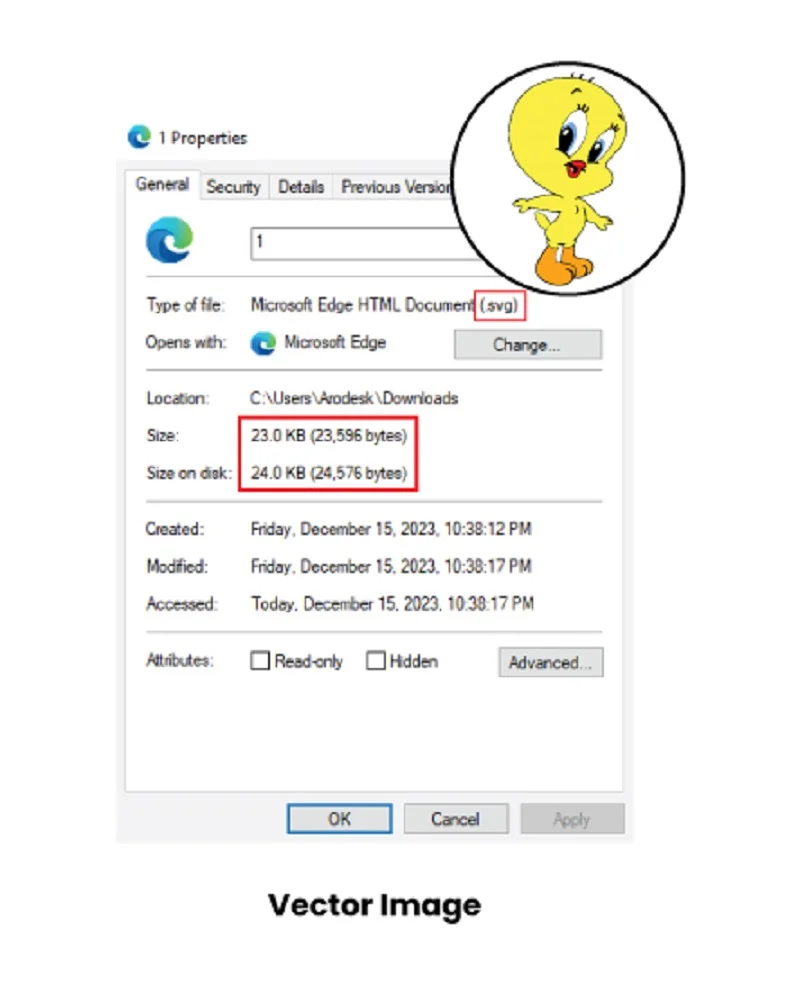
Vector images usually have smaller file sizes compared to raster images. Since it’s not dealing with lots of dots, the file size is usually smaller. It’s like saying, “Draw a line here” instead of explaining each dot’s color. Smaller files are handy because they’re quicker to share and don’t hog as much space.
Editing
Raster: Editing a picture made of tiny dots is a bit like fixing a painting with lots of small dots. If you want to change something small, it’s like adjusting those dots, and it can be a bit tricky. Also, if you try to make the picture bigger, those dots might get stretched, and your picture might not look as good.
Vector: Now, think of editing vector images like playing with digital building blocks. Since it uses math to describe shapes, you can easily move things around or make them bigger without any problems. It’s like having a plan that you can change without worrying about small dots. This makes it really good for fixing and adjusting designs without losing quality.
Use Cases
Raster:

Raster images are like your digital photos. They’re awesome when you need lots of details, like in a picture or a digital painting. Imagine using them for your vacation photos or a beautiful artwork you created on your computer. They’re great for things that stay the same size.
Vector:

Vector images are perfect when you want to use the same picture but in different sizes, like making a logo fit on a big computer screen or a small phone screen. Vectors are like magical images that can change sizes without losing their coolness. They’re fantastic for flexible projects, including designing business cards, where you might want the same logo to look awesome in various sizes.
Color Representation
Raster:
In a raster image, colors are created by blending tiny dots of different shades. Each dot has its own color, and when you put them together, you get the full picture. It’s like creating a painting where each stroke contributes to the overall color.
Vector:

Vector images use math to define colors. Instead of dealing with lots of dots, vectors describe colors using mathematical formulas. It’s like saying, “Use this formula to create this color here.” This precision in color definition makes vectors excellent for projects where you need exact and consistent color blends.
File Formats
Raster:
Raster images have special types, like JPEG for general use, PNG for keeping things clear (it even lets you see through some parts), and GIF for simple moving pictures. It’s like choosing different containers for your photos or graphics.
Vector:
Vector graphics also have their own types, such as SVG for web stuff or AI for Adobe Illustrator. These are like special containers for drawings or logos. They use a kind of digital language to describe shapes and lines. So, the picture stays super clear no matter how big or small you make it. It’s all about picking the right box for the kind of artwork you have.
Suggested Article-Vector File Formats
Software
Raster:

Raster images are the stars in programs like Photoshop. These programs are like digital darkrooms where you can edit each little dot in your pictures. So, if you want to add filters, adjust colors, or retouch photos, these are your go-to tools.
Vector:

Vector images find their home in software like Adobe Illustrator or Inkscape. It’s like having a digital drawing board where you can easily move and reshape things using mathematical instructions. Perfect for crafting logos, illustrations, or any design that needs flexibility without losing quality. Different software for different kinds of digital artwork!
Pros and Cons of Raster Images
Let’s talk about the good and not-so-good sides of raster images. Here’s a simple guide to the pros and cons of using raster images in the digital world!
Pros:
- Detailed and realistic.
- Rich color possibilities.
- Works everywhere.
- Great for precise edits.
Cons:
- Can’t stretch too much.
- File sizes can be big.
- Tricky detailed edits.
- Resolution stays fixed.
Pros and Cons of Vector Images
Vector images are like digital magic, but there are some things to keep in mind. We have pointed out some pros and cons of using vector images in the digital universe!
Pros:
- Infinitely scalable.
- Compact file sizes.
- Easy edits without loss.
- Resolution-independent flexibility.
Cons:
- Limited for detailed realism.
- Color options may be simpler.
- Software specificity.
- Complex for intricate designs.
When to Choose Raster or Vector Images?
Deciding between raster vs vector depends on your project’s needs. If you’re working on detailed stuff like really clear photos or things with a lot of details, go for raster images. They’re like super good at capturing how things really look. Also, if you want to make small changes to every tiny part of a picture or need a bunch of different colors, raster images, like JPEG or PNG, are the way to go.
But, if you need your picture to change sizes a lot without looking fuzzy, pick vector images. That’s where vector images shine. They’re like magic drawings that can be small or big without losing their coolness. If you want things to be simple, adaptable, and look good at any size, then vector images, like SVG or AI, are your friends. They’re great for being flexible without losing any sharpness in your designs.
Conclusion
We can see various sides of raster vs vector image. Raster images shine with detailed photos and vibrant colors, yet they struggle with flexibility in resizing. On the other side, vectors are like magic images that can resize easily, perfect for things like logos. “Vector vs Raster” is like the cool new trend in computer graphics, but both types still have their own cool spots. It’s like having different tools for different jobs, making our digital art and design world always interesting!
FAQs
Q1. What’s the main difference between raster and vector graphics?
Raster uses pixels in a grid for images, while vector uses math to create shapes, staying sharp no matter the size.
Q2. How does the choice impact image quality?
Choosing raster vs vector is like deciding between detailed dots and versatile, sharp graphics. Raster can lose quality when resized; vector stays sharp, no matter how big or small.
Q3. When is it good to use raster graphics?
Use raster for detailed images like photos, where every pixel matters.
Q4. When is vector graphics a better choice?
Choose vector for things that need to change size a lot, like logos or illustrations.
Q5. Do raster and vector impact file size differently?
Yes, raster files can be big, especially for high-res pics, while vector files are smaller and more efficient.
Q6. Can you use both in a design?
Absolutely! It’s like mixing the best of both worlds—sharp lines (vector) with detailed images (raster) to create designs that are both flexible and high-quality.










